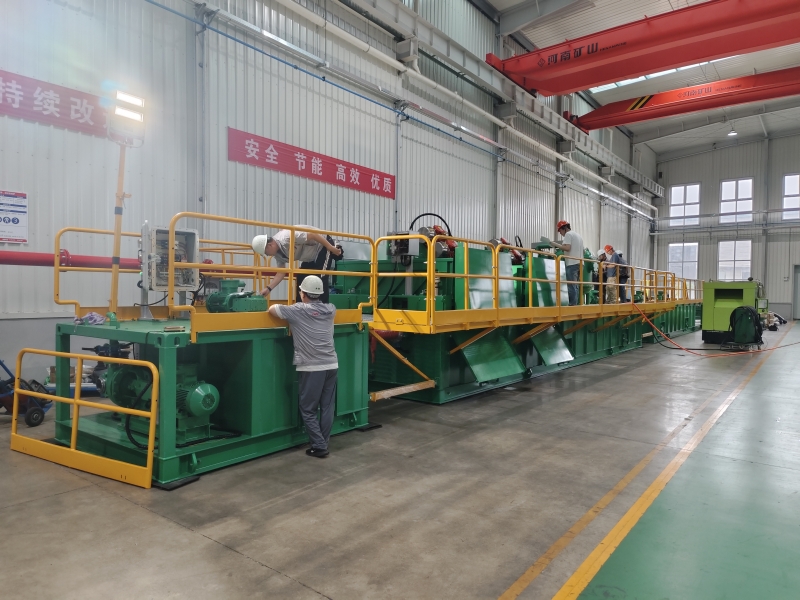
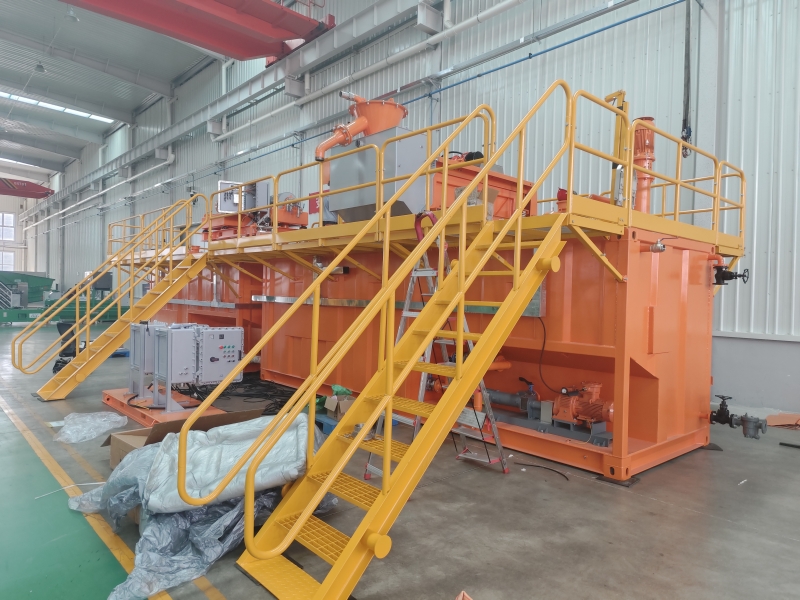
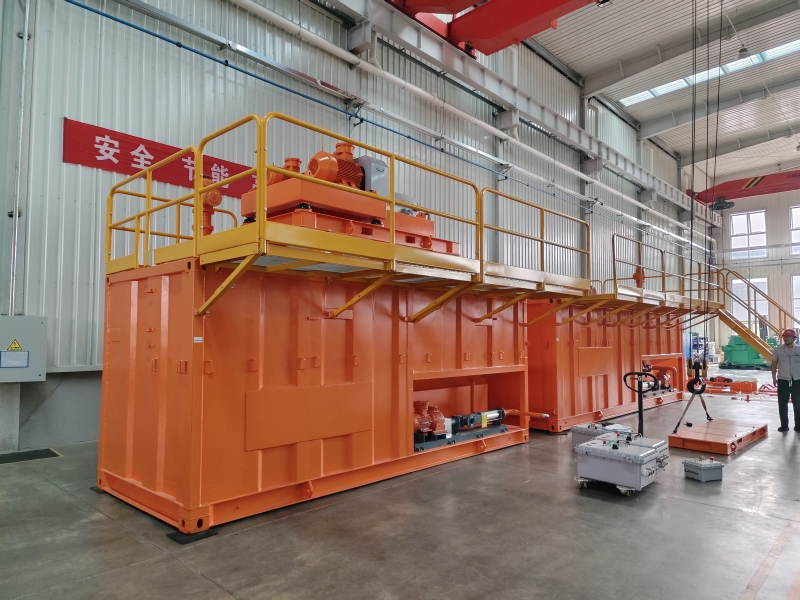
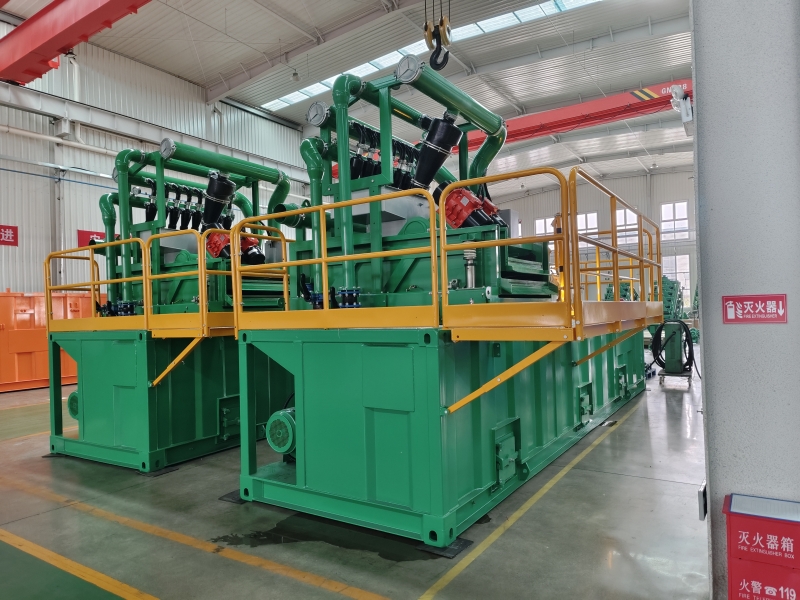
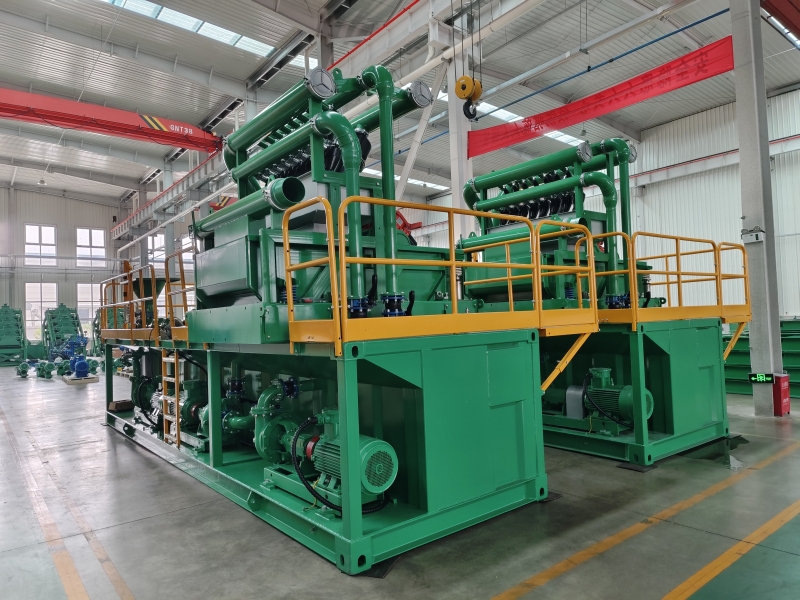
GN is a well-known brand from China, its full company name is HeiBei GN Solids Control Co.,Ltd which locadted in No.3 Industry Road, Dachang Chaobai River Development Area,Langfang, China; We are known around the world for unique innovation without compromise, sophistication while maintaining user simplicity, and superb service to our extremely wide customer base.specializing in supplying solids control& waste management equipment to the global market.
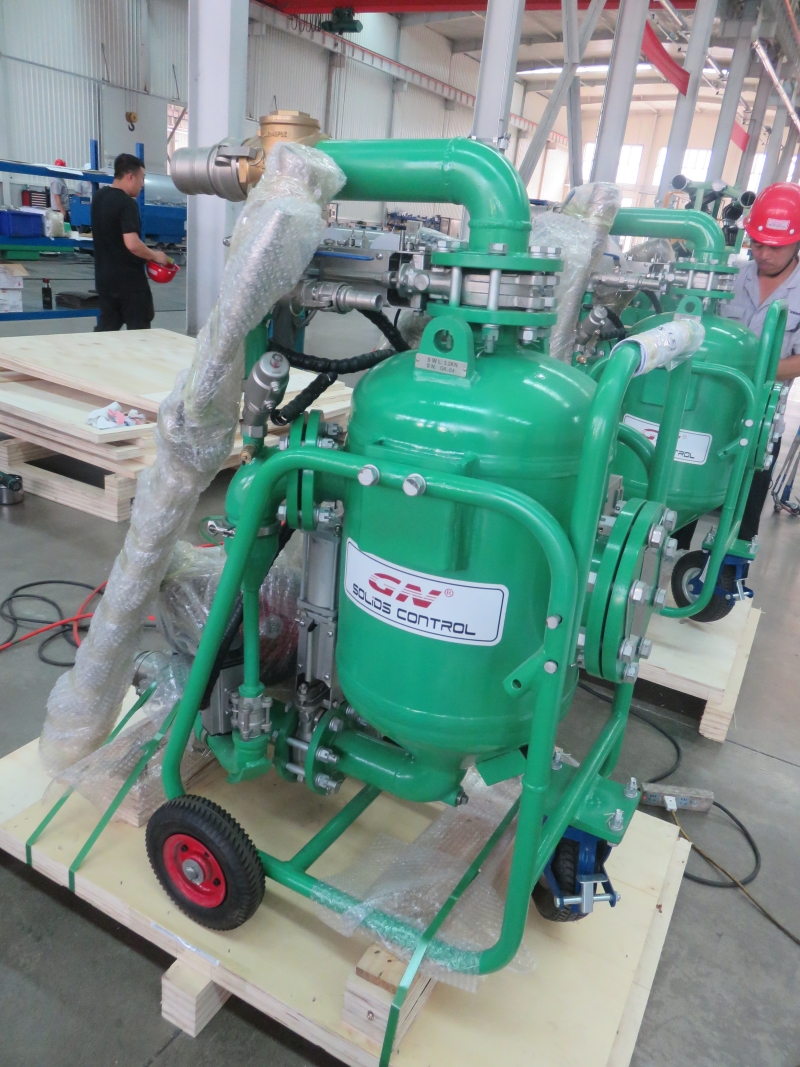
Vaccum Pump
A vacuum pump is a device that removes gas molecules from a sealed volume to create a partial vacuum. Here’s an overview of different types and their applications:
Types of Vacuum Pumps
- Positive Displacement Pumps: These work by mechanically trapping a volume of gas and moving it through the pump.
- Rotary Vane Pump: Uses a rotor with vanes that slide in and out. Commonly used for refrigeration, air conditioning, and laboratory applications.
- Diaphragm Pump: Uses a diaphragm to move the gas. Often used in chemical and pharmaceutical industries due to its ability to handle corrosive gases.
- Piston Pump: Utilizes pistons to compress and move gas. Used in various industrial applications.
- Momentum Transfer Pumps (Molecular Pumps): These work by transferring momentum to gas molecules.
- Turbo Molecular Pump: Uses a rapidly spinning rotor to impart momentum to gas molecules. Common in high-vacuum applications like semiconductor manufacturing.
- Diffusion Pump: Uses jets of vapor to push gas molecules out. Often used in high-vacuum environments for scientific research.
- Entrapment Pumps: Capture gases on solid surfaces within the pump.
- Cryopump: Uses very low temperatures to condense gases. Common in ultra-high-vacuum systems.
- Ion Pump: Uses a strong electric field to ionize gas molecules and capture them. Used in high-vacuum and ultra-high-vacuum applications.
Applications
- Industrial Processes: Employed in manufacturing processes like semiconductor production, coating, and metallurgy.
- Medical: Used in medical equipment such as vacuum-assisted wound closure devices and suction devices.
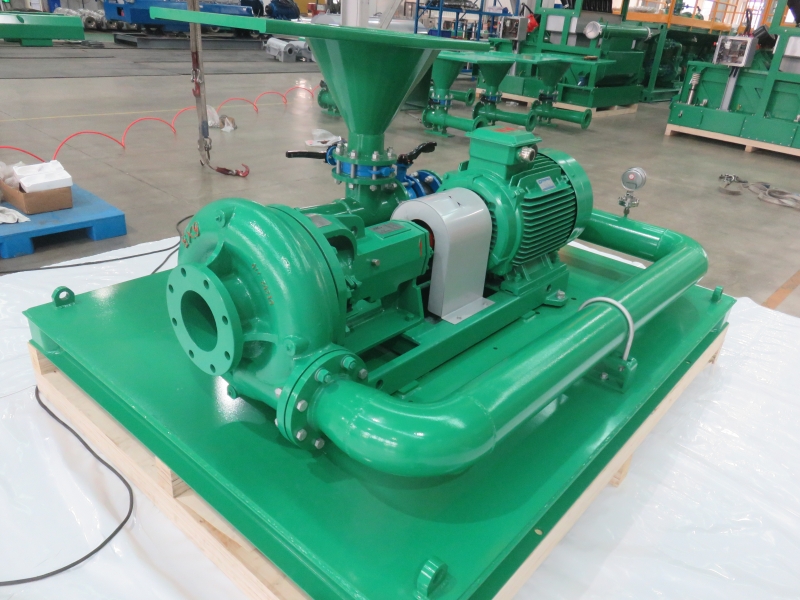
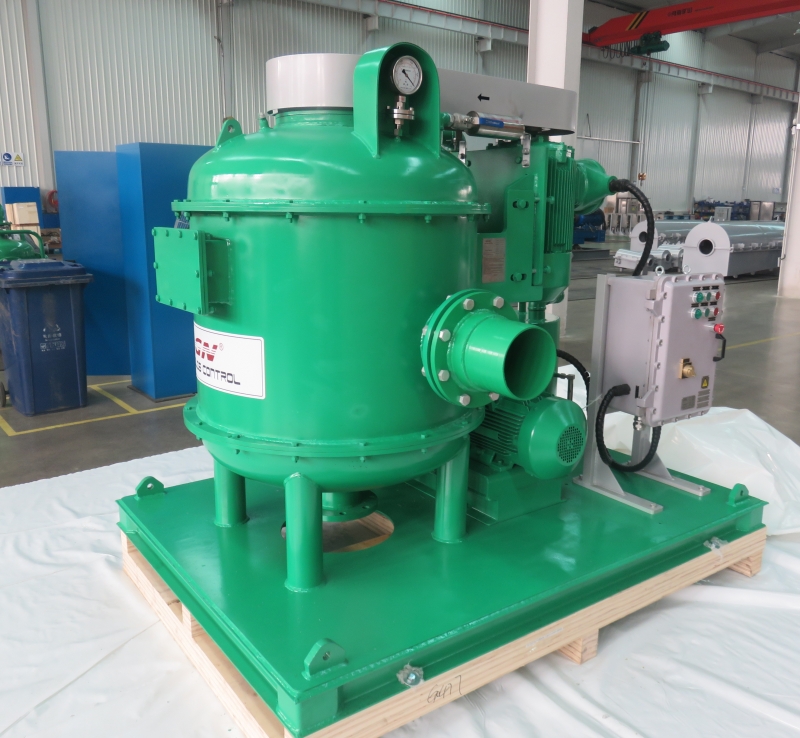
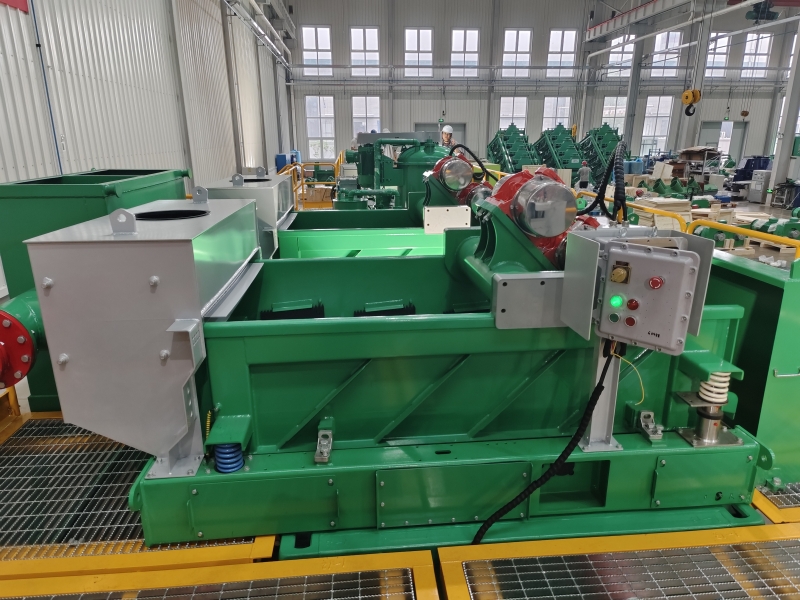
A vacuum degasser is a device used to remove dissolved gases from liquids. It is commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, food and beverage processing, and pharmaceuticals. Here’s a detailed overview of its functioning, types, and applications:
Functioning of a Vacuum Degasser
The primary function of a vacuum degasser is to remove gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other dissolved gases from liquids to improve product quality and prevent issues like oxidation or foaming. The basic working principle involves:
- Vacuum Application: The liquid to be degassed is exposed to a vacuum environment.
- Gas Removal: Under the vacuum, dissolved gases come out of the solution and are removed from the system.
- Repressurization: The degassed liquid is then repressurized to its original or desired pressure.
- Vertical Vacuum Degasser:
- Structure: Typically consists of a vertical cylindrical vessel.
- Application: Commonly used in the oil and gas industry to remove gas from drilling fluids.
- Horizontal Vacuum Degasser:
- Structure: Consists of a horizontal cylindrical vessel.
- Application: Often used in situations where vertical space is limited.
- Centrifugal Vacuum Degasser:
- Structure: Uses centrifugal force along with vacuum to remove gases.
- Application: Effective in high-throughput systems and for liquids with high gas content.
- Oil and Gas Industry:
- Drilling Fluids: Removing dissolved gases from drilling fluids to prevent gas cut and improve the accuracy of pressure measurements.
- Production: Degassing produced fluids to prevent issues in downstream processing and transport.
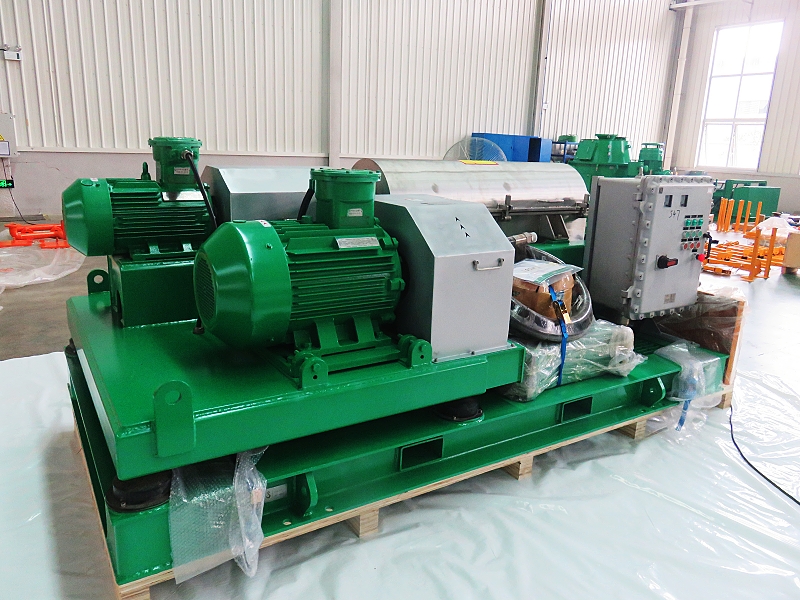
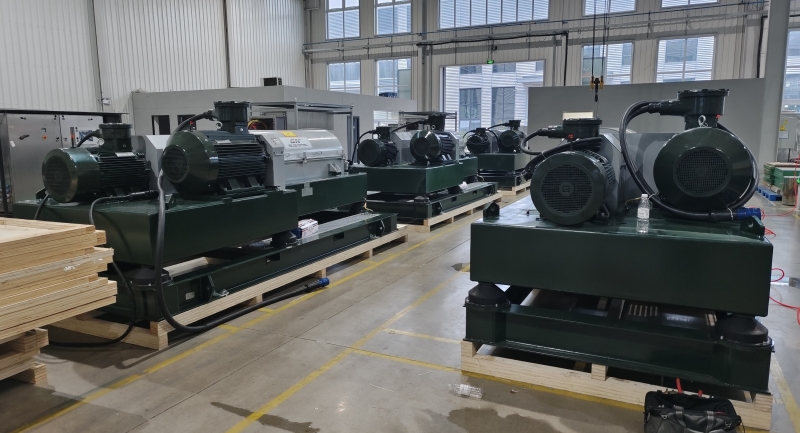
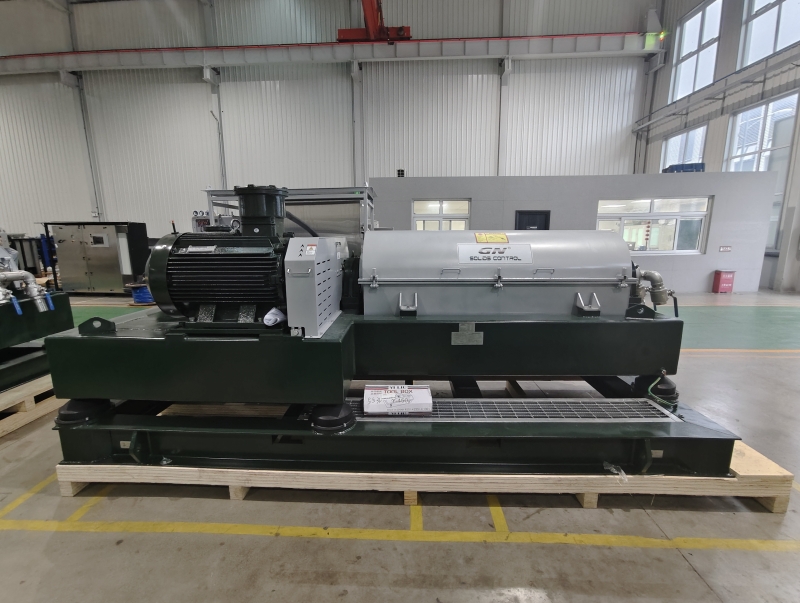
A decanter centrifuge is a piece of equipment used to separate solids from liquids in a slurry by applying centrifugal force. It is widely used in various industries, including wastewater treatment, oil and gas, food processing, and chemical manufacturing. Here’s an in-depth look at its working principle, components, types, and applications:
Working Principle
The decanter centrifuge operates on the principle of sedimentation, where centrifugal force accelerates the settling of solids:
- Feeding: The slurry is fed into the centrifuge through a feed inlet.
- Centrifugation: The slurry is subjected to high-speed rotation, generating centrifugal force.
- Separation: The centrifugal force pushes the solids to the outer wall of the bowl, forming a solid layer, while the clarified liquid (centrate) forms a layer closer to the center.
- Discharge: The separated solids are continuously removed by a screw conveyor, while the liquid phase is discharged through an outlet.
Components of a Decanter Centrifuge
- Bowl: A cylindrical or conical rotor that rotates at high speed.
- Screw Conveyor: A helical screw that rotates inside the bowl at a slightly different speed, conveying the solids toward the discharge end.
- Feed Inlet: Introduces the slurry into the bowl.
- Solids Discharge Outlet: Where the separated solids are expelled.
- Liquid Discharge Outlet: Where the clarified liquid exits the centrifuge.
- Drive System: Includes motors and gearboxes that control the rotational speeds of the bowl and screw conveyor.
- Control System: Monitors and controls the operational parameters for optimal performance.
- Horizontal Decanter Centrifuge:
- Structure: Features a horizontally oriented bowl.
- Application: Commonly used for large-scale industrial applications due to its high throughput and efficiency.
- Vertical Decanter Centrifuge:
- Structure: Features a vertically oriented bowl.
- Application: Used in applications where space is limited or for specific processes requiring vertical separation.
- 3-Phase Decanter Centrifuge:
- Function: Separates two immiscible liquid phases (e.g., oil and water) and a solid phase simultaneously.
- Application: Often used in the oil and gas industry and in food processing for separating oil, water, and solids.
Applications
- Wastewater Treatment:
- Sludge Dewatering: Removing water from sludge to reduce its volume and weight.
- Thickening: Concentrating sludge to increase solid content before further processing.
- Oil and Gas Industry:
- Drilling Mud Processing: Separating solids from drilling fluids to recycle the fluid and reduce waste.
- Crude Oil Clarification: Removing solid contaminants from crude oil.
- Food and Beverage Industry:
- Juice Production: Clarifying fruit and vegetable juices by removing pulp and other solids.
- Wine Making: Separating grape solids from must.
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries:
- Product Purification: Clarifying liquids by removing solid impurities.
- Waste Minimization: Reducing waste by separating valuable components from waste streams.
For our equipment brochure or more info, please visit our unique official website: www.gnsolidscontrol.com
MichaelSong
Sales manager
Whatsapp:+86 17801799913
E: michael@gnsolidscontrol.co/michael@gnsolidscontrol.com